In 2025, leveraging AI tools like ChatGPT will become a game-changer for marketers aiming to stay ahead in a hyper-competitive digital landscape. At the core of this transformation lies essential ChatGPT prompt engineering for marketing—a skill that enables professionals to craft precise, powerful prompts that drive better content, campaigns, and customer interactions.
This guide dives deep into ChatGPT prompt engineering for marketing, showing you how to turn simple inputs into high-converting outputs, streamline workflows, and unlock creative potential like never before.
What Is Prompt Engineering?
Prompt engineering involves crafting and refining inputs (prompts) to get the most accurate, relevant, and useful outputs from AI models—huge language models (LLMs) like GPT-4, Claude, Gemini, and others. It is crucial in human-AI interaction, particularly in natural language processing (NLP), generative AI tasks, and machine learning workflows.
Prompt engineering bridges the gap between human intent and machine understanding. Since LLMs do not inherently “understand” language the way humans do, phrasing a question or command can drastically influence the model’s response.
Anatomy of a Prompt: Elements and Techniques
A well-crafted prompt is the foundation for obtaining accurate, relevant, high-quality responses from AI systems. Whether you’re generating text, analysing data, or building a chatbot flow, understanding the structure of a prompt is essential. Let’s break down the anatomy of a prompt into its core elements and explore techniques to use them effectively.
1. Instructions
What it is?
Instructions define the task you want the AI to perform. This is the most direct part of the prompt — it tells the model what to do.
Examples
- “Summarise this article in two sentences.”
- “Write a professional email declining an offer.”
- “Translate this paragraph into French.”
Techniques
- Use action verbs (e.g., “Generate,” “Write,” “Explain,” “List”).
- Be specific — avoid vague phrasing.
- Use formatting like bullet points or numbered lists if the output should follow a structure.
2. Context
What it is:
Context provides background information that helps the AI understand the task more clearly. It may include the topic, target audience, tone, or additional details.
Examples:
- “The target audience is small business owners in the U.S.”
- “The tone should be casual and encouraging.”
- “Assume the user is a beginner with no technical experience.”
Techniques:
- Include relevant situational or audience details.
- Define tone or style explicitly (e.g., formal, persuasive, witty).
- Mention prior steps or previous conversations if continuity is essential.
3. Input Data
What it is:
Input data refers to the specific content or material the AI should use to generate its response. This can be a text snippet, table, question, or relevant dataset.
Examples:
- A product description is to be rewritten.
- A paragraph that needs to be analysed.
- A block of code that requires debugging.
Techniques:
- Separate the input from the rest of the prompt using delimiters like triple quotes (“””) or headings.
- Ensure the input is clean, relevant, and properly formatted.
- Provide only necessary data to avoid confusion.

4. Output Indicators
What it is:
Output indicators define how the response should be presented. This can include the format, length, tone, or specific elements.
Examples
- “Answer in bullet points.”
- “Limit your response to 100 words.”
- “Include at least one metaphor and a CTA.”
Techniques
- Mention the preferred format (e.g., table, list, paragraph).
- Set boundaries on length, detail, or complexity.
- Specify mandatory elements if needed.
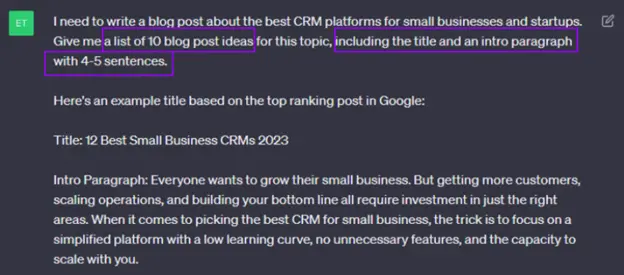
Putting It All Together: A Sample Prompt
Instructions: Write a short product description.
Context: This is for a sustainable fashion brand targeting Gen Z consumers who care about ethical production and eco-friendly materials.
Input Data: “Our new Tencel™ shirts are soft, breathable, and made from sustainably sourced eucalyptus pulp.”
Output Indicators: Keep it under 50 words, use a fun and approachable tone, and include the phrase “planet-approved.”
Result: “Meet your new fave tee — ultra-soft, breathable, and planet-approved. Crafted from Tencel™ and made with love for the Earth.”
Final Tips
- Always test and refine your prompt for optimal results.
- Combine structure with clarity and creativity.
- The better your prompt, the better your outcome.
Prompt Engineering Techniques
Prompt engineering refers to designing and optimising inputs (prompts) to guide AI models like GPT to generate sound, accurate, and contextually relevant outputs. Users can enhance the AI’s performance in specific tasks by carefully structuring prompts. Below are some commonly used prompt engineering techniques:
Zero-shot Prompt
A zero-shot prompt is when you ask the model to perform a task or answer a question without providing any prior examples or demonstrations. The model is expected to generalise based on its training data to provide the correct response.
How It Works: In a zero-shot prompt, the task is usually very clear, and the model’s ability to infer what’s required is key. The model leverages its understanding of language, context, and patterns from its pre-existing knowledge.
Example
- Prompt: “Translate the following sentence to French: ‘How are you today?'”
- Model Output: “Comment ça va aujourd’hui ?”
Advantages
- Simplicity: No need for prior examples.
- Versatility: Works for many tasks, assuming the model is trained on a relevant dataset.
Challenges
- The model may struggle with tasks that are too niche or require specific domain knowledge it wasn’t explicitly trained on.
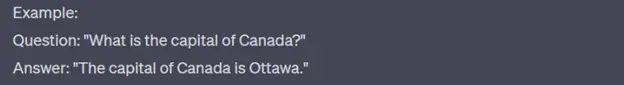
One-shot Prompt
A one-shot prompt provides the model with exactly one example of the task to guide its behaviour. The model is expected to learn the pattern or format from that single example and apply it to generate the appropriate output.
How It Works: One-shot learning is beneficial for tasks where the model needs more context to understand the pattern. By providing one example, you demonstrate the format, tone, or type of output you expect.
Example
- Prompt: “Translate the following sentence to French. Example: ‘Hello’ -> ‘Bonjour’. Now translate: ‘Good morning’.”
- Model Output: “Bonjour.”
Advantages
- Improved Accuracy: A more straightforward guide to the AI on what’s expected.
- Efficiency: Only one example is necessary, making it simpler than providing many.
Challenges
- Limited Context: The model only has a single example to generalise from, which might limit its ability to handle more complex task variations.

Few-shot Prompt
A few-shot prompt provides the model with several examples of the task or query it needs to perform. The more examples provided, the better the model can discern patterns and generate accurate outputs.
How It Works: Few-shot learning allows the model to observe multiple instances of the task, enabling it to learn the underlying structure and apply that learning to new, unseen cases.
Example
- Prompt: “Translate the following sentences to French. Example 1: ‘Hello’ -> ‘Bonjour’.
- Example 2: ‘Good morning’ -> ‘Bonjour’. Example 3: ‘Good night’ -> ‘Bonne nuit’. Now translate: ‘Good afternoon’.”
- Model Output: “Bon après-midi.”
Advantages
- Better Performance: Providing multiple examples gives the model more context, improving its accuracy in complex tasks.
- Flexibility: Allows for a broader range of tasks and more nuanced responses than zero-shot or one-shot.
Challenges
- Example Overload: Too many examples can overwhelm the model, reducing efficiency.
- Dependence on Quality: The model may still produce poor results if examples are not representative.

Chain-of-Thought Prompts
Chain-of-thought prompts involve guiding the model through a reasoning process step-by-step, helping it break down the problem into smaller, more manageable chunks. This approach can be beneficial for tasks that require logical reasoning, such as solving math problems or analysing complex scenarios.
How It Works: In a chain-of-thought prompt, the model must explicitly show its thinking process before providing a final answer. This allows the model to maintain coherence and avoid jumping to conclusions.
Example
- Prompt: “To solve the math problem, break it down step-by-step. First, add 2 + 3. Then, subtract 1. Now multiply by 4. What is the final result?”
- Model Output:
- “Step 1: 2 + 3 = 5.”
- “Step 2: 5 – 1 = 4.”
- “Step 3: 4 * 4 = 16.”
- “The final result is 16.”
Advantages
- Improved Accuracy: The model is less likely to make mistakes by providing a detailed reasoning process.
- Transparency: It’s easier to understand how the model concluded, making the output more interpretable.
Challenges
- Cognitive Load: The model can sometimes get bogged down in unnecessary steps, leading to less efficient reasoning.
- Complexity: Constructing prompts that guide the AI effectively through the process might require more effort.

Each technique serves a distinct purpose based on the complexity of the task and the need for contextual understanding. Zero-shot prompts are ideal for simpler tasks or those with well-defined answers, while one-shot and few-shot prompts provide more context to improve accuracy.
Chain-of-thought prompts are particularly beneficial for tasks requiring logical reasoning or step-by-step problem-solving. By selecting the appropriate prompt engineering technique, you can guide AI models to produce higher-quality outputs, improving efficiency and accuracy.
Tips for Effective Prompt Engineering
Effective prompt engineering is essential for getting the best output from AI models. Crafting well-structured prompts can greatly enhance the quality and accuracy of the responses you receive. Here’s a detailed guide on how to approach prompt engineering effectively:
1. Be Clear and Specific in Your Wording
Clarity and specificity are the foundation of prompt engineering. When you write a prompt, it should directly convey what you expect from the model. The more precise your prompt, the less ambiguity the AI will face in interpreting it, which leads to better outcomes.
- Avoid Vague Terms: Phrases like “tell me about X” or “give me an answer” are too general and could lead to a broad response. Instead, specify precisely what you’re looking for, e.g., “Summarise the key points from the article on X” or “Provide a detailed comparison of A vs. B.”
- Use Proper Keywords: Focus on essential terms that reflect what you’re looking for. For example, instead of asking, “Can you explain AI?”, specify, “Can you explain how AI is used in marketing?” This helps narrow the scope.

2. Provide Examples in Your Prompt
Examples help clarify your expectations, especially if you’re looking for specific responses or formats. By providing a sample output or framing your request with examples, you guide the AI to the kind of result you’re hoping to achieve.
- Demonstrate Format: If you want the answer in a specific format (e.g., a list, table, essay, etc.), show the model what that format looks like. For example, “Write a list of five points about X, formatted like this: 1. Point 1, 2. Point 2.”
- Example of Desired Tone or Style: If you need a response in a particular tone (formal, casual, technical, etc.), provide an example sentence. For instance, “Write this in a professional tone like the following example: ‘The report concludes that…'”

3. Focus on What You Want It To Do
Clearly define the task you want the AI to complete. If you ask a vague question like “What are the benefits of using AI?”, the model might give a broad, general answer. Instead, focus on a task or purpose. For instance:
- Clarify the Task’s Purpose: Instead of asking “What is SEO?”, rephrase it to be more task-focused, like “Describe how SEO strategies can improve website traffic for small businesses.”
- Give Action-Oriented Instructions: Make sure to specify the kind of action or outcome you’re looking for. For example, “Create a bullet-point summary of this article” or “Generate a creative campaign idea for a coffee shop.”

4. Testing and Experimenting with Prompts
Not every prompt will yield the best results on the first try. Effective prompt engineering often involves trial and error, tweaking your prompt until you get the desired output. The key is to be open to refining your approach and adapting based on the results you receive.
- Iterate for Refinement: Start with a simple version of your prompt and gradually add more details. This allows you to assess which elements of the prompt lead to better responses and which parts might need adjustment.
- Analyse the Model’s Responses: After testing, evaluate how well the model followed your instructions and whether it understood the nuances of your request. Use this feedback to revise the prompt and experiment with different phrasings, detail levels, or examples.
- Use Variations: Try different angles if one way of phrasing the prompt doesn’t work. For instance, if asking “What is AI?” returns a general answer, try “Explain AI in the context of business automation.”
Bonus Tips for Effective Prompt Engineering
- Specify Context: Include relevant background information in your prompt if the task requires context. For instance, if you’re asking for advice on digital marketing, mention the industry or business type to get more tailored suggestions.
- Avoid Overloading: While detail is essential, overloading the prompt with too many instructions can confuse the AI. Try to keep prompts concise while still providing enough context and direction.
- Use Feedback Loops: Continuously refine prompts based on the results from the model’s outputs. This helps create a feedback loop that makes your prompts more efficient over time.
By following these tips, you can craft more effective prompts that lead to more precise, relevant, and useful AI-generated responses.
Prompt Engineering for Marketers and Content Creators
Prompt engineering is crafting well-structured and specific prompts to get the best possible output from AI models like ChatGPT. For marketers and content creators, mastering prompt engineering can significantly enhance productivity, creativity, and engagement with AI tools.
Here’s a guide customised to marketers and content creators:
1. Understand Your Goal
Before crafting a prompt, clarify your end objective. Are you producing social media content, blog posts, or ad copy? Knowing the goal helps in forming the correct prompt. For example, “Create an engaging Instagram post introducing a new product targeting eco-conscious consumers.”
2. Be Specific and Clear
Specificity is key. Include details such as tone, style, target audience, and any keywords or phrases to be included. For instance, “Write a 200-word blog post for a tech company offering AI software for small businesses. Use a professional tone and highlight its efficiency benefits.”
3. Use Instructions and Constraints
Marketers often require content with specific constraints like word count, structure, or key points. For example, “Write a 150-word email newsletter, focusing on three benefits of using our service, with a strong call to action.”
4. Incorporate Brand Voice and Style
Ensure the content aligns with your brand’s voice, whether fun, professional, or quirky. For example, “Write a product description for luxury skincare in an elegant and aspirational tone.”
5. Leverage AI for Multiple Drafts
AI can provide several drafts or variations for comparison. For example, “Generate three variations of a Facebook ad targeting young adults looking for workout apparel: one humorous, one inspirational, and one focusing on sustainability.”
6. Create Engaging Headlines and Hooks
Prompt AI to generate multiple headline options for blog posts or articles. For example, “Give me 5 headline ideas for a blog post about the latest social media trends in 2025.”
7. Focus on Use Cases
Customised prompts to the content format, whether it’s for blog posts, social media, or email campaigns. For example, “Write a blog post on the impact of artificial intelligence in content creation” or “Create a Twitter thread outlining best practices for Instagram ads.”
8. Refine and Iterate
AI-generated content can often be refined. After getting the initial output, ask, “Can you make this more concise?” or “Rewrite this with a more conversational tone.”
9. Experiment with Different Tools
Explore various AI tools, such as those for image generation, SEO writing, or video scripts. For example, “Create a 30-second script for a video ad promoting a fitness app, focusing on tracking and convenience.”
10. Measure and Analyse AI Output
Track engagement and performance metrics of AI-generated content, such as click-through rates or social media interactions, to see what resonates best with your audience.
By mastering these strategies, marketers and content creators can optimise their workflows, stay creative, and deliver high-quality content more efficiently. Would you like help formulating prompts for any specific project you’re working on?
Why Chatgpt is a Game-Changer in Marketing
In the ever-evolving world of digital marketing, the introduction of AI-driven tools like Chatgpt has revolutionised how businesses interact with customers. One of the most significant advancements is the role of essential Chatgpt prompt engineering for marketing, which has proven to be a game-changer in how marketers strategise, engage with audiences, and streamline processes.
What is Chatgpt Prompt Engineering for Marketing?
At its core, Chatgpt prompt engineering for marketing involves creating effective, targeted prompts that can optimise Chatgpt’s responses to cater to specific marketing goals. From generating personalised content to automating customer support, how marketers design these prompts directly impacts the quality and relevance of the AI-generated output.
Key Benefits of Chatgpt in Marketing
- Personalised Customer Engagement: With the right prompts, Chatgpt can craft highly personalised messages, emails, and advertisements, allowing businesses to connect more deeply with their audience.
- Content Generation at Scale: Whether it’s blog posts, social media updates, or ad copy, Chatgpt prompt engineering for marketing enables the quick generation of high-quality content, saving time and resources.
- Enhanced Customer Support: Chatgpt can be engineered to handle customer queries, providing real-time responses and solutions that elevate the customer experience and support your marketing efforts.
- Data-Driven Insights: Using AI-powered tools like Chatgpt, marketers can gain valuable insights from large datasets, helping them refine their strategies and create targeted campaigns based on customer preferences.
- Automation and Efficiency: Chatgpt can automate repetitive tasks such as answering FAQs or drafting responses, allowing marketing teams to focus on higher-level strategy and creativity.
Why It Matters in Marketing
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, having a tool that can quickly adapt to different marketing needs is essential. The use of essential ChatGPT prompt engineering for marketing allows businesses to harness AI’s power to create content, analyze trends, engage customers, and drive conversions with minimal manual effort.
By mastering the art of prompt engineering, marketers can fine-tune ChatGPT to meet specific business objectives, improving brand tone, increasing engagement, or enhancing lead generation. This level of adaptability makes Chatgpt an indispensable asset for modern marketing strategies.
In conclusion, Chatgpt’s potential in marketing goes beyond just generating content—it provides endless opportunities for optimisation and efficiency, making it a must-have tool for marketers aiming to stay ahead in a competitive marketplace.
Essential ChatGPT Prompts for Marketing Success
ChatGPT becomes truly powerful when paired with the right prompts. Crafting targeted, strategic prompts can help marketers generate compelling copy, plan campaigns, perform audience analysis, and more. Here are examples and categories of essential prompts:
Content Creation
- “Write a blog post about [topic] in a friendly yet informative tone.”
- “Generate 10 catchy headlines for a social media post promoting [product/service].”
Audience Engagement
- “What are 5 frequently asked questions that a potential customer might have about [product]?”
- “Draft a reply to a negative customer review that maintains professionalism and empathy.”
Campaign Strategy
- “Create a 7-day email marketing sequence for launching a new digital product.”
- “Outline a content calendar for 1 month focused on promoting [theme or product].”
SEO Optimization
- “Suggest SEO keywords for a blog targeting [audience] about [topic].”
- “Rewrite this blog to improve its readability and SEO: [insert content].”
Branding & Tone of Voice
- “Develop brand messaging pillars for a sustainable clothing brand.”
- “Create a voice and tone guide for a luxury skincare brand.”
Implementing ChatGPT in Your Marketing Strategy
Integrating ChatGPT into your overall marketing approach can automate repetitive tasks, spark creative ideas, and optimize performance. Here’s how to incorporate it strategically:
- Content Generation & Planning:
Use ChatGPT to produce high-quality content at scale—blogs, newsletters, captions, scripts, etc. Pair it with keyword research tools for SEO content planning. - Social Media Marketing:
Automate caption creation, schedule ideas, hashtag research, and audience responses. ChatGPT can simulate brand voice and help you maintain consistency across channels. - Email Marketing:
Leverage AI to draft personalized, conversion-focused emails. Use prompts for A/B testing subject lines, crafting CTAs, and segmenting audiences effectively. - Market Research & Insights:
Ask ChatGPT to simulate buyer personas, generate competitor analysis outlines, and even predict trends based on available data. - Ad Copywriting & A/B Testing:
Generate multiple versions of ad copy quickly to test variations across different platforms like Google Ads, Facebook, or LinkedIn. - Chatbot Integration:
Use GPT-powered bots for customer service, lead generation, FAQs, and onboarding. It enhances engagement and reduces human workload.
Boost Your Marketing with AI
AI in marketing isn’t just a trend—it’s a performance driver. Leveraging tools like ChatGPT can enhance productivity, creativity, and decision-making.
- Speed & Scale: AI enables marketers to scale content efforts without increasing headcount. Whether it’s 100 product descriptions or 50 social posts, it cuts turnaround time drastically.
- Personalization: AI can customise messages to different segments, improving click-through and conversion rates. ChatGPT can simulate customer personas and adjust content tone accordingly.
- Data-Driven Decisions: AI helps analyze large datasets to extract trends, predict behavior, and suggest action plans—making campaigns more precise and measurable.
- Innovation & Experimentation: Use ChatGPT for brainstorming new ideas—campaign concepts, angles, product names, or customer journey enhancements. It acts as a creative collaborator.
- Cost Efficiency: By automating content, customer interaction, and planning, AI reduces reliance on large teams and external agencies, cutting costs without compromising quality.
Unlocking Marketing Excellence Through Prompt Engineering
In 2025, marketers who master ChatGPT prompt engineering won’t just keep up with the competition—they’ll lead it. This guide has shown that crafting clear, targeted, and strategic prompts is the key to unlocking AI’s full creative and operational potential. From generating content at scale to tailoring messaging for specific audiences, prompt engineering transforms ChatGPT from a smart assistant into a powerful marketing partner.
As AI continues to evolve, those who invest in refining their prompt-building skills will find themselves not only saving time but also creating smarter, more impactful campaigns. The future of marketing belongs to those who know how to talk to machines—and get results.